Introduction
Cloud computing is no longer a future concept—it is the foundation of how modern digital systems are built, deployed, and scaled. From streaming platforms and mobile apps to enterprise software and artificial intelligence, nearly every digital service today runs on cloud infrastructure. At the center of this transformation are AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, the three platforms that define the global cloud computing landscape.
Understanding AWS Azure Google Cloud is essential for businesses, IT professionals, and students who want to stay relevant in a technology-driven world. These platforms provide on-demand access to computing power, storage, networking, databases, security, and advanced services such as AI and analytics—without the need to manage physical hardware. This shift has fundamentally changed how organizations innovate, scale, and compete.
This guide offers a comprehensive and practical exploration of AWS Azure, and Google Cloud, covering their architecture, core services, pricing models, security frameworks, use cases, and global infrastructure. Whether you are new to cloud computing or looking to deepen your understanding of major cloud platforms, this article will help you make informed decisions and build a strong foundation in cloud technology.
By the end of this guide, you will clearly understand how AWS Azure Google Cloud deliver cloud services, what differentiates them, and why mastering these platforms is critical for modern IT careers and enterprise success.
What Are AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud?
Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) are the world’s leading public cloud platforms that provide on-demand computing resources over the internet.
These platforms allow organizations to:
- Run applications without owning servers
- Store massive volumes of data securely
- Scale infrastructure globally within minutes
- Pay only for what they use
Together, AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud form the backbone of modern digital infrastructure.
Understanding Cloud Computing Through AWS, Azure & GCP
Cloud computing becomes easier to understand when viewed through AWS Azure Google Cloud because they implement cloud concepts at global scale.
Through these platforms, cloud computing delivers:
- On-demand self-service
- Broad network access
- Resource pooling
- Rapid elasticity
- Measured service
Each provider applies these principles using massive global data centers and automation technologies.
Key Differences Between AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud
Although AWS Azure Google Cloud offer similar services, they differ in strengths and enterprise focus.
| Feature | AWS | Azure | Google Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|
| Market Share | Largest | Strong Enterprise | Fast-Growing |
| Hybrid Cloud | Moderate | Excellent | Moderate |
| AI & ML | Strong | Strong | Industry-Leading |
| Pricing | Flexible | Enterprise-friendly | Cost-optimized |
Understanding these differences helps organizations choose the right platform—or adopt multi-cloud strategies.
Core Services of AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform
All three platforms provide similar core cloud services, which form the foundation of modern cloud environments.
Core Categories
- Compute services
- Storage services
- Networking services
- Database services
- Security and identity services
Despite different naming conventions, the functionality remains comparable across AWS, Azure, and GCP.
Cloud Computing Models Explained Using AWS, Azure & GCP
Cloud computing models define how services are delivered.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Virtual machines
- Storage
- Networking
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Application runtime
- Middleware
- Developer tools
Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Fully managed applications
- No infrastructure management
AWS, Azure, and GCP support all three models, enabling flexibility across industries.
AWS Azure Google Cloud: Architecture and Service Comparison
Cloud architecture is built on regions, availability zones, and edge locations.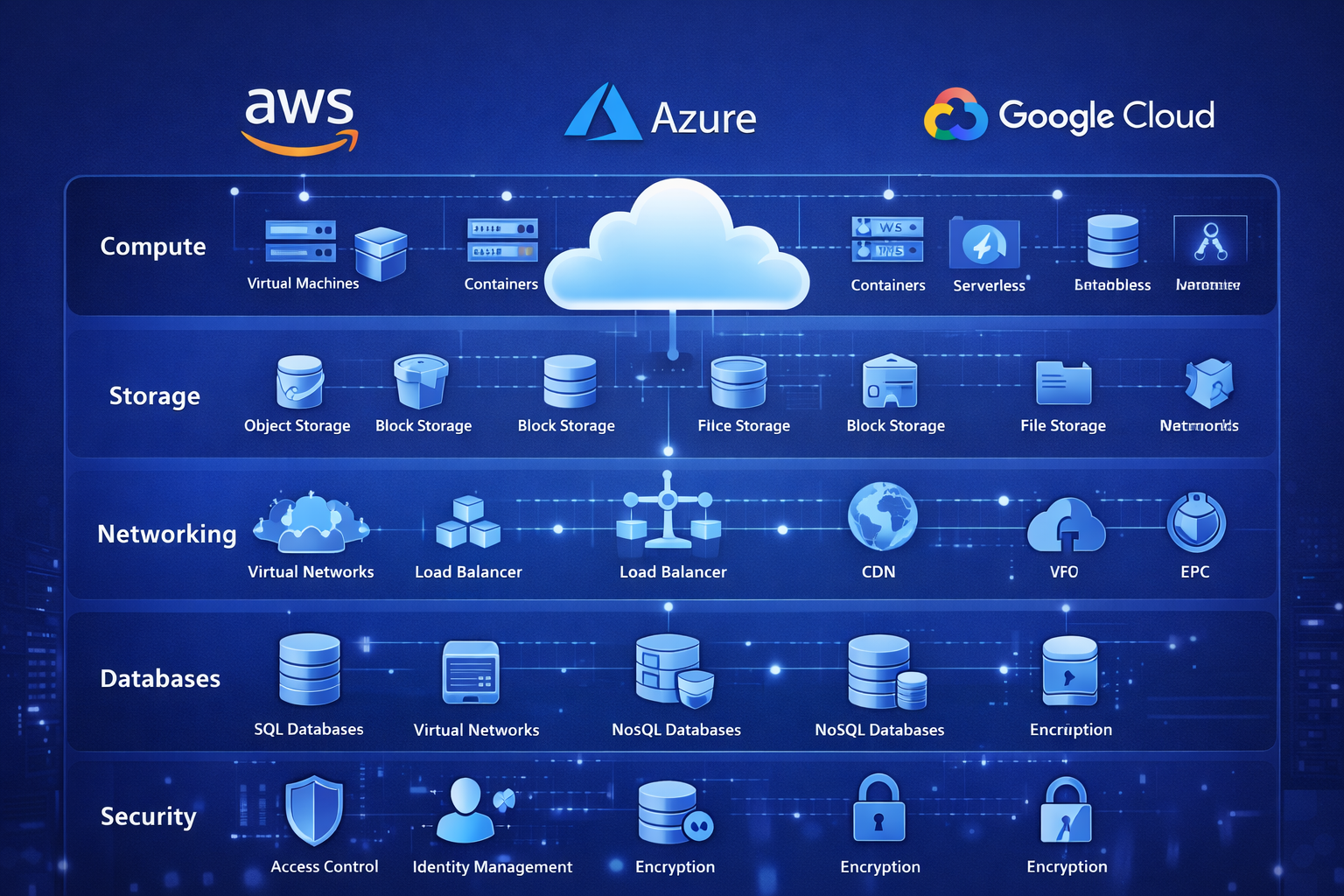
Architectural Similarities
- Fault-tolerant design
- High availability
- Automated scaling
- Distributed networking
Architectural Differences
- Azure excels in hybrid integration
- AWS offers the widest service catalog
- GCP provides superior internal networking performance
Public Cloud Platforms: AWS Azure Google Cloud
AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud are classified as public cloud platforms because:
- Infrastructure is owned by the provider
- Resources are shared securely across customers
- Access is delivered via the public internet
Public cloud platforms are ideal for scalability, speed, and innovation.
How AWS Azure Google Cloud Deliver Cloud Services
Cloud services are delivered using:
- Web-based management consoles
- APIs
- Command-line tools
- Infrastructure-as-Code
This delivery model allows rapid deployment, automation, and consistent environments across development and production.
Compute, Storage, and Networking in AWS Azure Google Cloud
Compute
- Virtual Machines
- Containers
- Serverless functions
Storage
- Object storage
- Block storage
- File storage
Networking
- Virtual private networks
- Load balancers
- Content delivery networks
These components work together to run modern applications efficiently.
Security and Compliance in AWS Azure Google Cloud
Security is a shared responsibility between provider and customer.
Built-in Security Features
- Identity and Access Management
- Data encryption
- Network firewalls
- Monitoring and logging
All three platforms comply with global standards such as ISO, SOC, and GDPR.
Pricing Models of AWS Azure Google Cloud
Pricing is usage-based and flexible.
Common Pricing Options
- Pay-as-you-go
- Reserved instances
- Spot pricing
- Sustained-use discounts
Effective cost management is critical to cloud success.
Use Cases of AWS Azure Google Cloud Platform
Common Use Cases
- Web and mobile application hosting
- Big data analytics
- AI and machine learning
- Backup and disaster recovery
- DevOps and CI/CD pipelines
From startups to governments, cloud platforms power digital transformation globally.
Global Infrastructure of AWS Azure Google Cloud
Each provider operates dozens of global regions and hundreds of data centers.
Benefits
- Low latency
- High availability
- Disaster recovery
- Regulatory compliance
Global infrastructure enables businesses to serve customers worldwide reliably.
Learn Cloud Platforms the Right Way
AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud are no longer optional skills—they are core IT competencies. Understanding their services, architecture, pricing, and use cases is essential for modern IT professionals.
Start Your Cloud Career with Cambridge Infotech
Gain hands-on AWS Azure Google Cloud training, real-world projects, and expert mentorship at Cambridge Infotech.
Real-World Architecture Patterns Using AWS Azure Google Cloud
To truly understand how AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud operate in production, it’s important to look at real-world cloud architecture patterns. Most enterprises don’t just deploy a single virtual machine; they design distributed, fault-tolerant systems.
Common Architecture Patterns
- Three-tier architecture (Web, Application, Database)
- Microservices architecture
- Event-driven architecture
- Serverless architecture
- Hybrid cloud architecture
In all three platforms, these architectures rely on:
- Load balancers to distribute traffic
- Auto-scaling to handle demand
- Managed databases for reliability
- Monitoring tools for observability
For example, an e-commerce application might host its frontend on scalable compute services, backend APIs on container platforms, and databases in managed relational services. This architecture ensures high availability and performance during traffic spikes.
DevOps and Automation Across AWS Azure Google Cloud
DevOps is one of the strongest reasons organizations adopt cloud platforms. AWS Azure Google Cloud provide native tools that enable continuous integration, continuous delivery (CI/CD), and infrastructure automation.
Key DevOps Capabilities
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
- Automated testing and deployment
- Continuous monitoring
- Faster release cycles
Popular Tools Used
- Terraform
- Git-based CI/CD pipelines
- Container orchestration platforms
- Cloud-native monitoring services
Cloud DevOps reduces manual errors, improves deployment speed, and ensures consistency across environments.
Learn hands-on DevOps tools with cloud platforms at
Containers and Kubernetes in AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud
Containers have become a standard way to build and deploy applications. All three cloud platforms provide managed Kubernetes services that simplify container orchestration.
Why Containers Matter
- Lightweight and portable
- Faster application startup
- Environment consistency
- Ideal for microservices
Kubernetes enables:
- Automated scaling
- Self-healing applications
- Rolling updates
- Load balancing
Organizations using Kubernetes on cloud platforms gain flexibility to deploy applications across environments with minimal changes.
Data, Analytics, and Big Data Platforms
Modern organizations generate massive amounts of data. AWS Azure Google Cloud provide advanced analytics tools to process and analyze this data at scale.
Analytics Capabilities
- Data warehouses
- Streaming data processing
- Business intelligence dashboards
- Real-time analytics
Common Use Cases
- Customer behavior analysis
- Fraud detection
- Predictive analytics
- IoT data processing
Cloud-based analytics platforms eliminate the need for expensive on-premise data warehouses and allow businesses to analyze data in real time.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Cloud Platforms
One of the fastest-growing areas in cloud computing is AI and machine learning. Cloud platforms make AI accessible without requiring deep expertise in model training or infrastructure management.
AI Services Include
- Pre-trained AI APIs
- Custom model training
- Natural language processing
- Computer vision
- Recommendation engines
These services enable organizations to integrate intelligence into applications such as chatbots, recommendation systems, and predictive models.
Cloud Networking Explained in Depth
Networking is the backbone of cloud infrastructure. AWS Azure Google Cloud provide virtual networking that mimics traditional networks but with far more flexibility.
Networking Components
- Virtual networks / VPCs
- Subnets
- Route tables
- Internet gateways
- Firewalls and security groups
Advanced networking allows:
- Secure isolation of workloads
- Hybrid connectivity with on-premise data centers
- Multi-region deployments
Understanding cloud networking is critical for designing secure and high-performance applications.
Identity, Access Management, and Governance
Managing who can access cloud resources is essential. Each cloud platform provides robust identity and access management (IAM) systems.
IAM Capabilities
- User and role management
- Fine-grained permissions
- Multi-factor authentication
- Integration with enterprise directories
Good governance ensures:
- Compliance with regulations
- Reduced security risks
- Clear accountability
IAM is one of the most important skills for cloud administrators and architects.
Backup, Disaster Recovery, and High Availability
Cloud platforms offer powerful tools for data protection and disaster recovery.
Disaster Recovery Strategies
- Backup and restore
- Pilot light
- Warm standby
- Multi-region active-active
Cloud-native disaster recovery is faster, more reliable, and far more cost-effective than traditional approaches.
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies
Many organizations use more than one cloud platform. Hybrid and multi-cloud strategies provide flexibility and reduce vendor lock-in.
Why Organizations Choose Multi-Cloud
- Regulatory requirements
- Performance optimization
- Cost control
- Risk reduction
Cloud platforms support secure connectivity between environments, allowing organizations to design complex but resilient architectures.
Industry-Specific Cloud Use Cases
Cloud adoption varies by industry, but its impact is universal.
Examples
- Healthcare: Secure patient data and analytics
- Finance: Fraud detection and high-availability systems
- Education: Online learning platforms
- Retail: Scalable e-commerce systems
- Manufacturing: IoT and predictive maintenance
Cloud platforms adapt to industry needs through specialized compliance and security features.
Cloud Skills and Career Opportunities
Cloud computing skills are among the highest-paying IT skills globally.
Popular Job Roles
- Cloud Engineer
- Cloud Architect
- DevOps Engineer
- Site Reliability Engineer
- Cloud Security Specialist
Employers value professionals who understand multiple cloud platforms rather than just one.
Build job-ready cloud skills with Cambridge Infotech
Certifications and Learning Pathways
Certifications validate cloud knowledge and improve employability.
Certification Levels
- Fundamentals
- Associate
- Professional / Expert
A structured learning path usually includes:
- Cloud fundamentals
- Core services
- Architecture
- Security and networking
- DevOps and automation
Hands-on practice is essential to truly master cloud platforms.
Cost Optimization and Cloud Financial Management
Cloud costs can grow quickly if not managed properly.
Best Practices
- Monitor usage regularly
- Use auto-scaling
- Delete unused resources
- Choose the right pricing models
Cloud cost management tools help organizations optimize spending while maintaining performance.
Cloud Governance, Policies, and Compliance
Large organizations implement governance frameworks to manage cloud usage.
Governance Includes
- Resource tagging
- Policy enforcement
- Audit logging
- Compliance reporting
Governance ensures that cloud adoption remains secure, compliant, and cost-effective.
The Future of Cloud Computing
The cloud ecosystem continues to evolve rapidly.
Emerging Trends
- Edge computing
- AI-driven cloud operations
- Serverless-first development
- Green and sustainable cloud
- Industry cloud platforms
Cloud platforms will continue to shape how software is built and delivered.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What are AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud?
AWS Azure Google Cloud are leading cloud computing platforms that provide on-demand access to computing resources such as servers, storage, databases, networking, security, and analytics over the internet. They help organizations build, deploy, and scale applications without managing physical infrastructure.
2. Why are AWS Azure Google Cloud important?
AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud are important because they power most modern digital services. They enable scalability, cost efficiency, global access, high availability, and faster innovation for businesses of all sizes, from startups to large enterprises.
3. How do AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud work?
These cloud platforms operate through globally distributed data centers. Users access cloud services via web consoles, APIs, or command-line tools, while the provider manages hardware, maintenance, security, and scaling automatically.
4. What are the main differences between AWS Azure Google Cloud?
The main differences lie in service strengths and ecosystem focus:
AWS offers the widest range of services and has the largest market share
Azure integrates strongly with Microsoft products and excels in hybrid cloud
Google Cloud is known for data analytics, AI, and high-performance networking
Each platform suits different business and technical needs.
5. What services are common across AWS Azure Google Cloud?
All three platforms offer core cloud services such as:
Compute (virtual machines, containers, serverless)
Storage (object, block, and file storage)
Networking (virtual networks, load balancers)
Databases (SQL and NoSQL)
Security and identity management
Conclusion: Master the Cloud with Confidence
AWS Azure Google Cloud are the foundation of modern digital infrastructure. From startups to enterprises, these platforms enable scalability, security, and innovation at an unprecedented scale.
Understanding their services, architecture, pricing, security, and use cases is no longer optional—it is essential for anyone pursuing a career in IT or digital transformation.
Take the Next Step with Cambridge Infotech
Get hands-on training, real-world projects, and expert mentorship in AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.






